Colon cancer is one of the few tumors that can be diagnosed early before noticing any symptoms
Colorectal cancer is the most frequent malignant tumor in Spain and the second highest mortality, both in men and women. In Spain, 32,000 new cases are diagnosed per year and for this cause more than 14,000 people die annually. Despite its incidence and mortality, it is one of the most approachable and, diagnosed in time, is curable in more than 90% of cases.
Acoording to doctor Pedro Bretcha , president of the Spanish Society of Surgical Oncology (SEOQ) and specialist in surgical oncology at the Hospital Quirónsalud Torrevieja
, president of the Spanish Society of Surgical Oncology (SEOQ) and specialist in surgical oncology at the Hospital Quirónsalud Torrevieja , it is possible to reduce or eliminate risk factors, especially those related to food, to alcohol, tobacco and physical exercise or lifestyle.
, it is possible to reduce or eliminate risk factors, especially those related to food, to alcohol, tobacco and physical exercise or lifestyle.
- Food: diets rich in animal fats (red meat) and poor in fiber can increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
-
Physical inactivity: a sedentary life favors the risk of this disease.
- Tobacco use: increases the risk of suffering from polyps, which are usually the precursors of this tumor.
- Consumption of alcohol: it seems that alcoholic beverages favors the growth of the cells of the mucosa of the colon, giving rise to the manifestation of polyps.
The vast majority of colon cancers are sporadic, with hereditary being the minority. People with a first-degree relative with cancer have a higher risk of suffering from it, as well as having had a cancer previously or determined type of polyps before age 60. It is also verified that the danger increases with age: 90% are diagnosed after 50 years and, as it gets older, it increases.
Stool analysis is as effective as colonoscopy in detecting cancer
Doctor José Farré Alegre, Head of General Surgery and Gastroenterology and Oncology Surgery specialist at Hospital Quirónsalud Torrevieja explains that, "as regards its early detection, there is a consensus that all those without risk factors who should undergo a study from 50 years of age. There are several types of tests: a colonoscopy every 10 years, a CT colonography every five years, a sigmoidoscopy every five years, or a blood test hidden in the stools every year that has proven to be as effective as other diagnostic tests. In contrast, those with an increased risk should enter a study program at a younger age and more frequently. People who have a first-degree relative under 60 with colon cancer or two first-degree relatives at any age, should have a colonoscopy from 40 years or 10 years before diagnosis of the family member; and from that moment, every five years.
In contrast, those with an increased risk should enter a study program at a younger age and more frequently. People who have a first-degree relative under 60 with colon cancer or two first-degree relatives at any age, should have a colonoscopy from 40 years or 10 years before diagnosis of the family member; and from that moment, every five years.
Those whose first-degree relative is diagnosed beyond the age of 60, or who have two or more affected second-degree relatives, should have a colonoscopy study starting at age 50. On the other hand, those who have a relative of second or third degree affected by colon cancer would go on to the usual studies of the normal population.
Current events
Current events
- 24 de abril de 2024
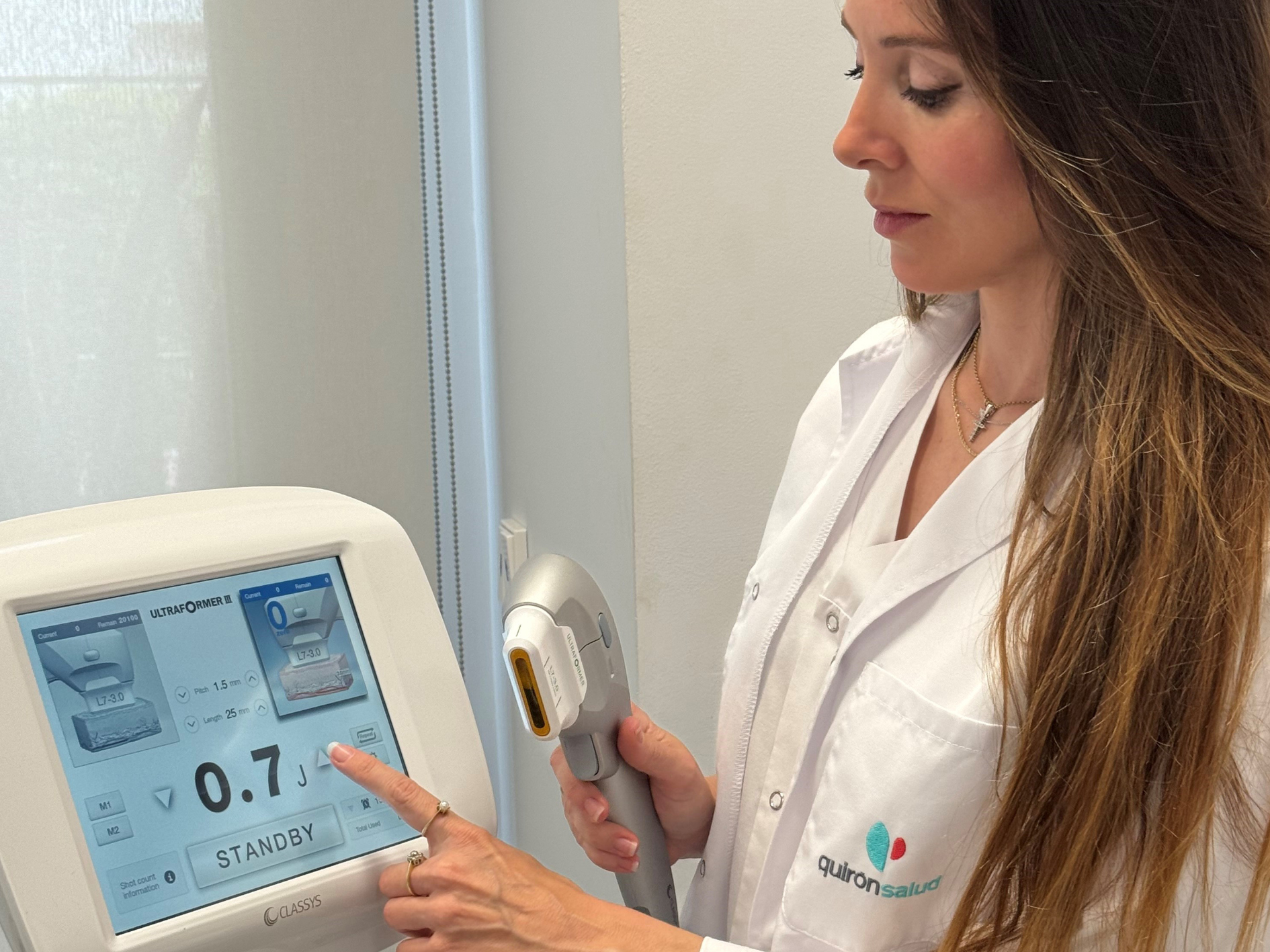
Ultrasonido de alta intensidad, el innovador tratamiento sin cirugía de rejuvenecimiento facial que no...
• Basado en ultrasonidos, no deja signos visibles tras el tratamiento por lo que permite hacer vida normal horas después de la sesión y se puede aplicar en los meses de veran...Hospital Quirónsalud Marbella - 24 de abril de 2024
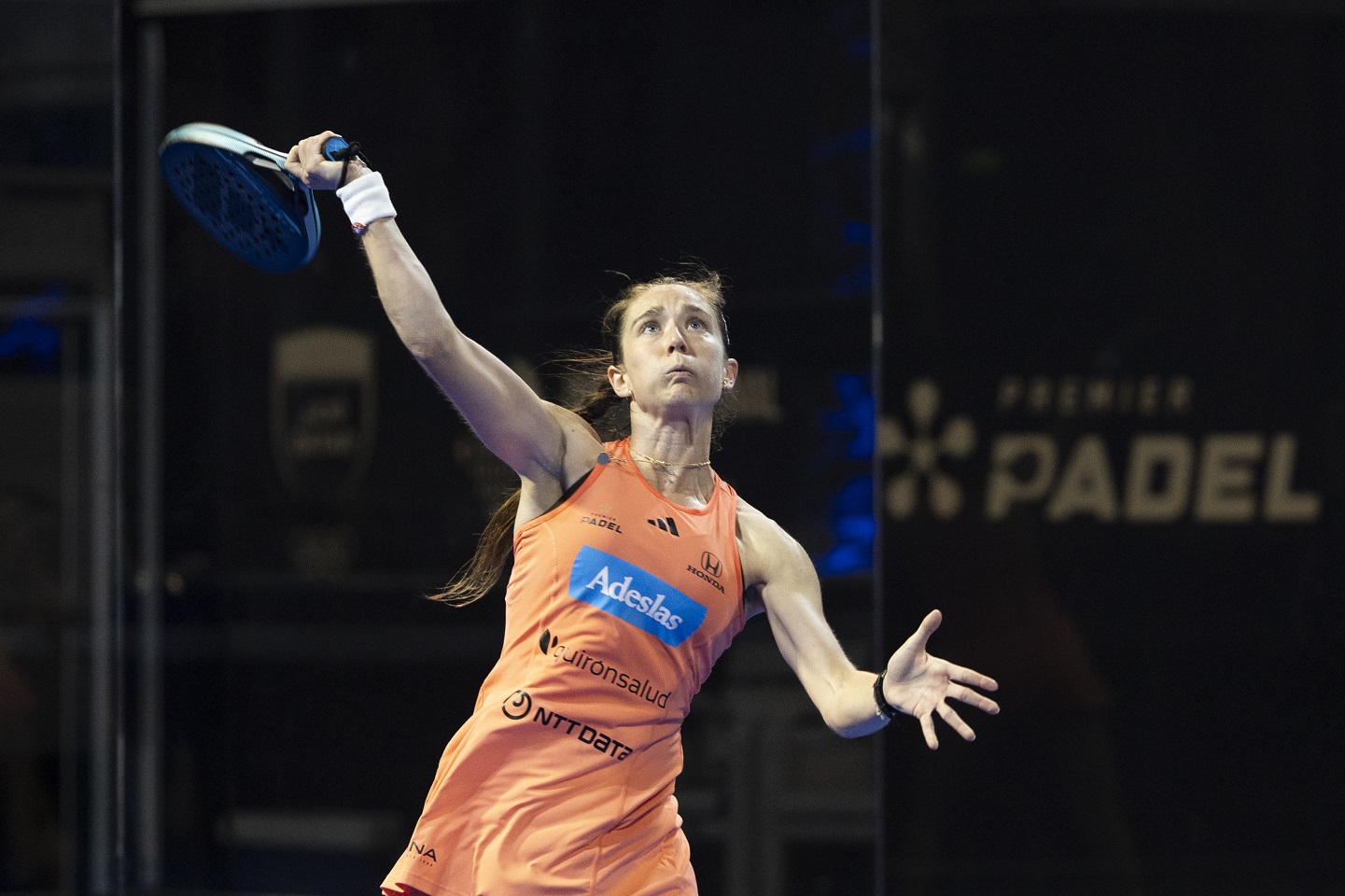
Quirónsalud, Servicio Médico Oficial del Premier Padel Andalucía Sevilla P2
El torneo, que se disputa del 28 de abril al 5 de mayo, reúne a las principales figuras de este deporte, a nivel nacional e internacional.Quirónsalud - 24 de abril de 2024
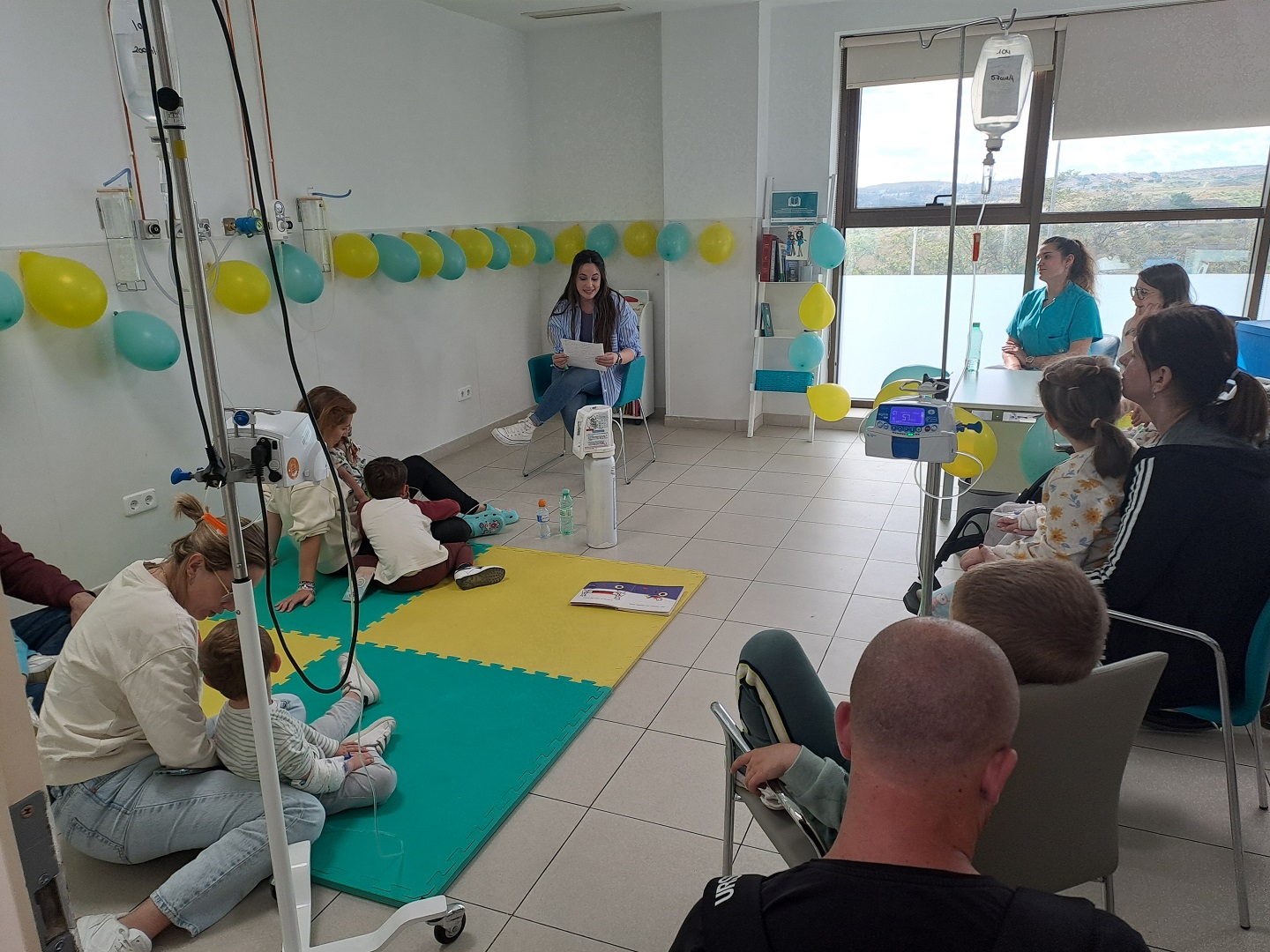
El Hospital Quirónsalud Toledo celebra el Día del Libro con la lectura de ‘Las aventuras de Kenko’
Evadir del ámbito hospitalario, hacer disfrutar con la lectura y fomentar los hábitos saludables, los objetivos de la iniciativa.Hospital Quirónsalud ToledoPediatría y sus Áreas Específicas - 24 de abril de 2024
El Centro Médico Quirónsalud Valdebebas ofrece la posibilidad de conocer la edad metabólica
· Durante los viernes 26 de abril y 10 de mayo en horario de 9.00 a 14.00 horas y los miércoles 8 y 22 de mayo en horario de 15.00 a 20.00 horas. · Las personas interesadas q...Centro Médico Quirónsalud ValdebebasEndocrinología y Nutrición - 23 de abril de 2024
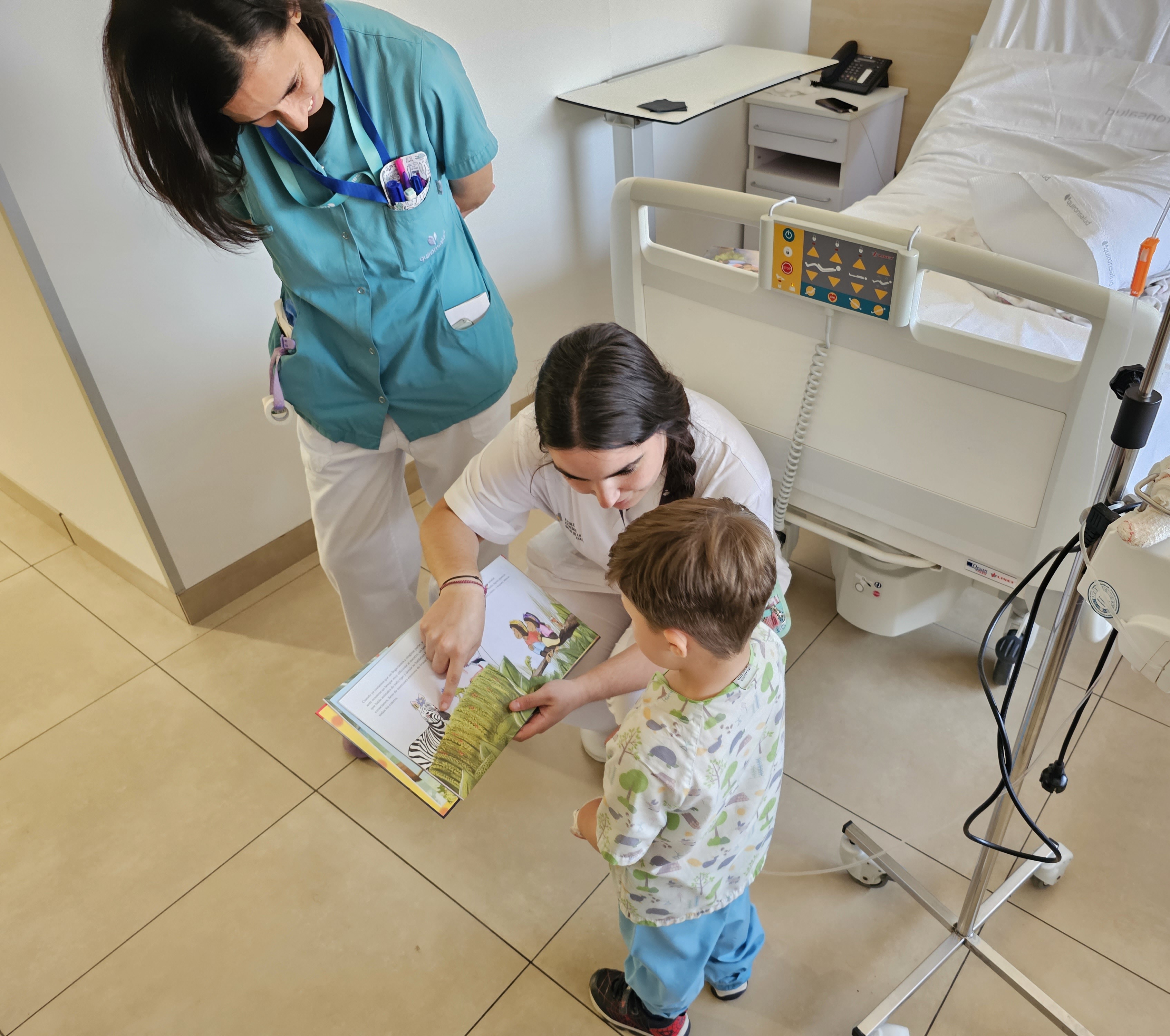
Quirónsalud Infanta Luisa celebra el Día del Libro con sus pacientes hospitalizados para promover los...
Quirónsalud Infanta Luisa regala libros a sus pacientes hospitalizados buscando amenizar así su estancia hospitalariaHospital Quirónsalud Infanta LuisaLogopedia - 24 de abril de 2024
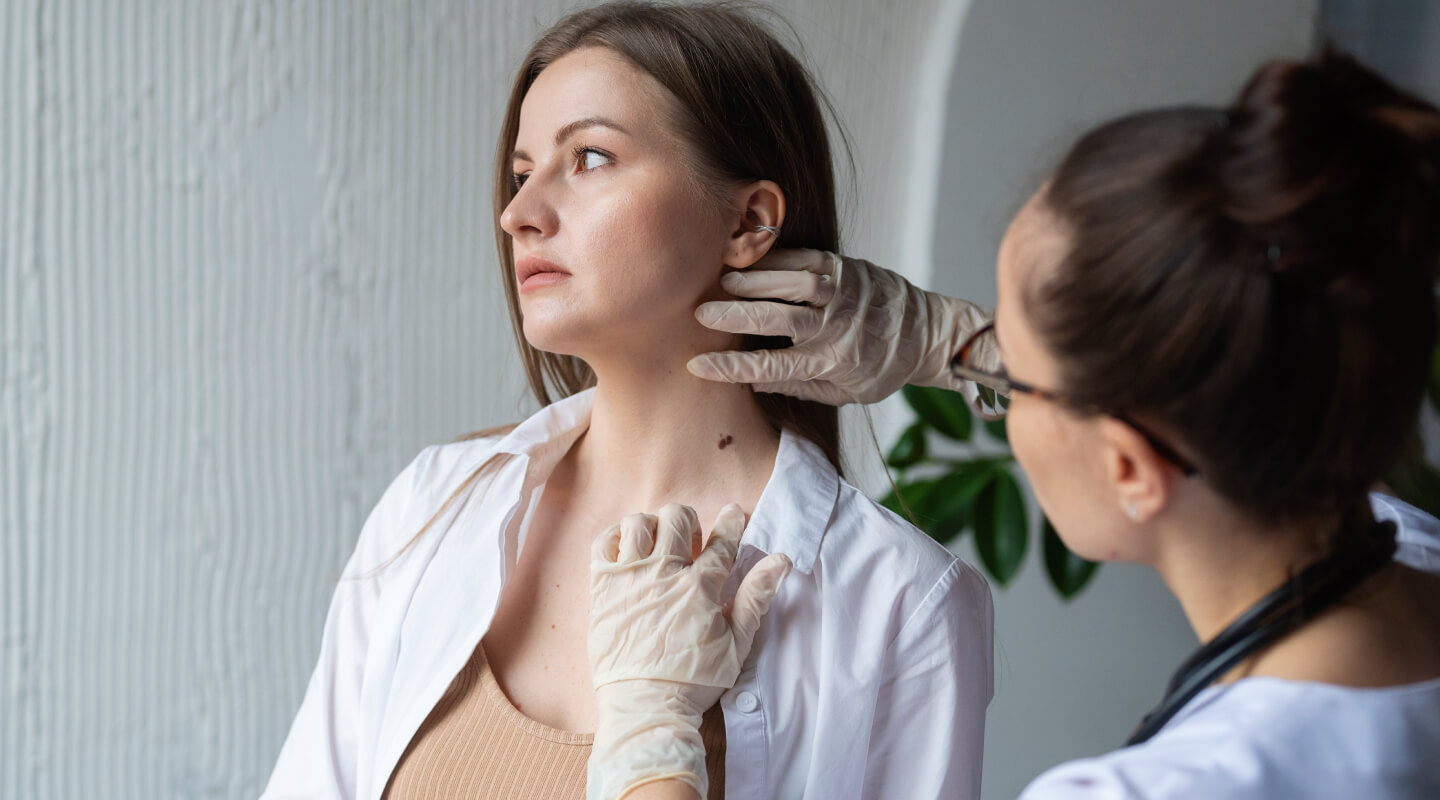
El Hospital Quirónsalud Badalona incorpora un nuevo servicio de Teledermatología para acelerar el diagnóstico...
El nuevo servicio agiliza la atención y respuesta médica, en 48 horas, posibilitando una actuación rápida sobre las lesiones que presenten indicios de malignidad.Hospital Quirónsalud BadalonaDermatología Médico-Quirúrgica y Venereología - 23 de abril de 2024
La Fundación Jiménez Díaz obtiene la acreditación de calidad más reconocida en estudios genéticos, la...
La acreditación, otorgada por la ENAC, refleja la calidad y buenas prácticas del Departamento de Genética del hospitalHospital Universitario Fundación Jiménez Díaz - 22 de abril de 2024
La Fundación Jiménez Díaz obtiene la certificación de calidad más avanzada en sus servicios de UCI Quirúrgica,...
La acreditación es una norma internacional de gestión de la calidad de los cuidados críticosHospital Universitario Fundación Jiménez Díaz - 23 de abril de 2024
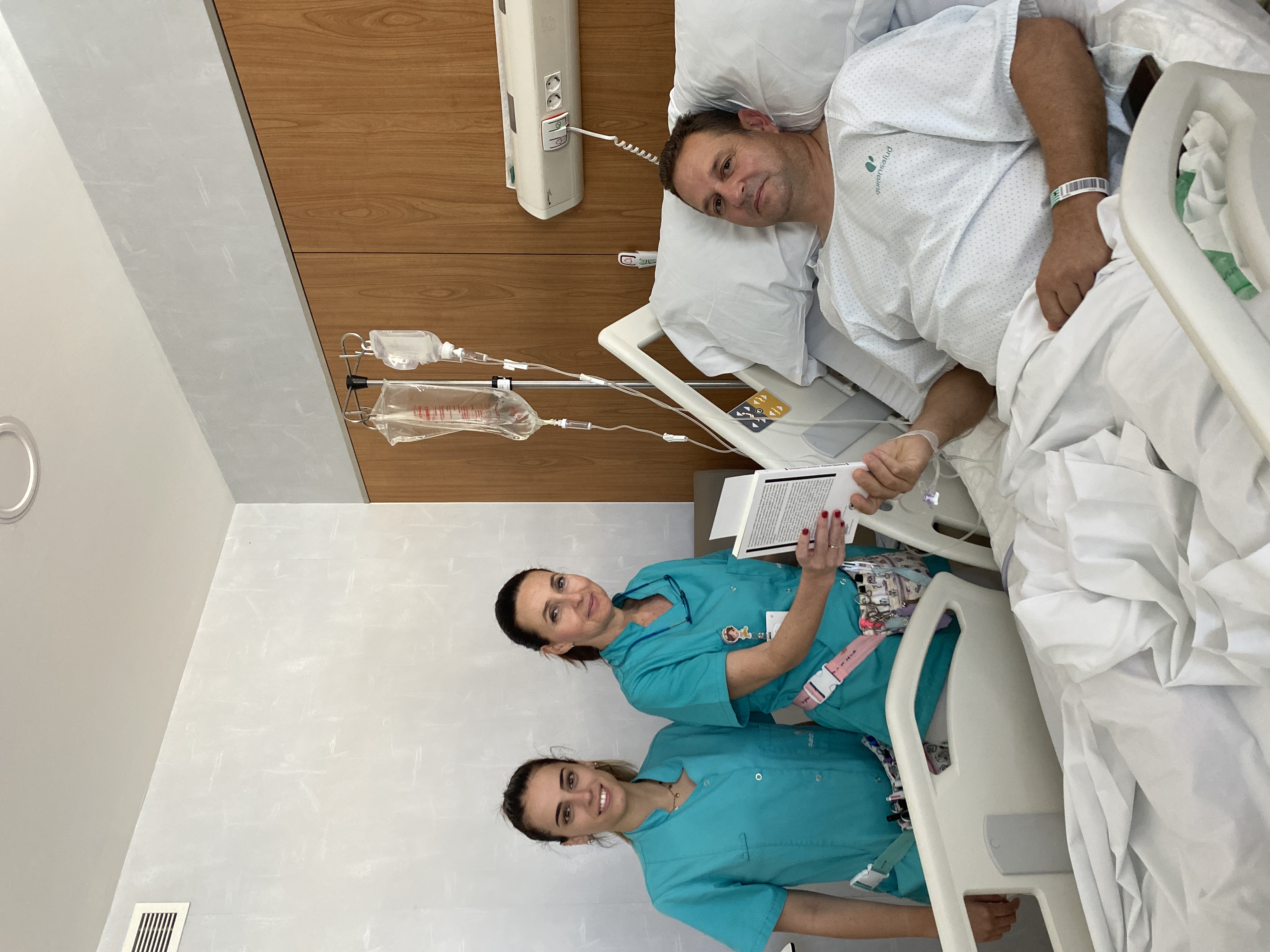
Quirónsalud Málaga celebra el Día del Libro con sus pacientes
El personal de Enfermería ha repartido ejemplares cortesía de la Fundación Quirónsalud.Hospital Quirónsalud Málaga - 23 de abril de 2024
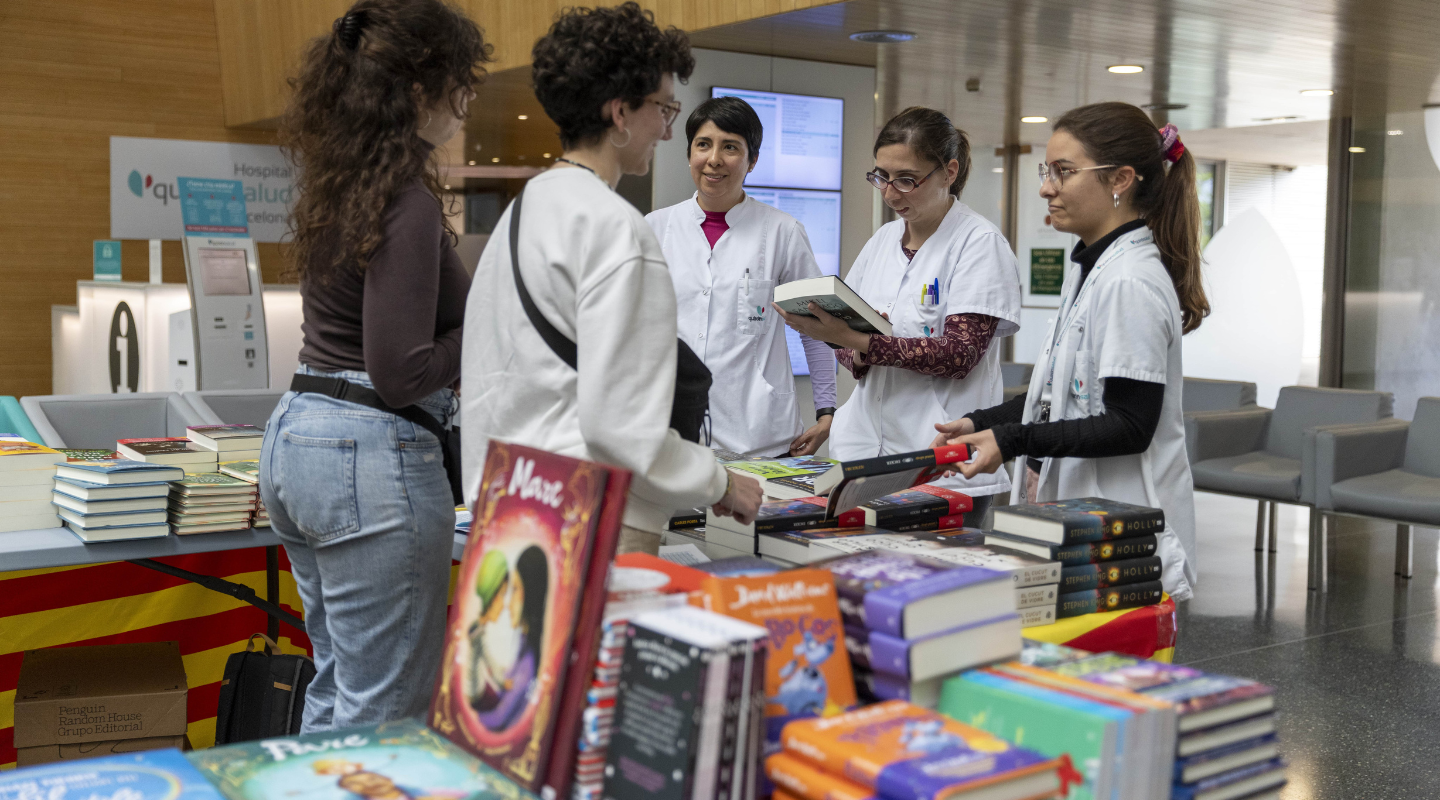
Celebramos Sant Jordi con Parada de libros y reparto de rosas
Hoy 23 de abril celebramos Sant Jordi en Quirónsalud Barcelona con el tradicional reparto de rosas y por primera vez con el estreno de una parada de libros tanto para trabaja...Hospital Quirónsalud Barcelona - 23 de abril de 2024
El Hospital Quirónsalud Campo de Gibraltar regala libros a sus pacientes por el Día Internacional del...
El centro de Palmones promueve la lectura entre sus pacientes hospitalizados para tratar de hacer más amena su estancia en el hopspitalHospital Quirónsalud Campo de Gibraltar - 23 de abril de 2024
Quirónsalud Huelva celebra el Día del Libro con sus pacientes hospitalizados
Con motivo del Día Internacional del Libro que se celebra hoy, el Hospital Quirónsalud Huelva ha querido celebrar esta fecha obsequiando a sus pacientes hospitalizados con un...Hospital Quirónsalud Huelva - 23 de abril de 2024
La cirugía con quimioterapia e hipertermia y el uso de dianas moleculares: lo último en oncología
Málaga acoge la II Jornada Nacional Multidisciplinar de Innovación en Cáncer con la participación de más de 100 especialistas en la materiaHospital Quirónsalud MálagaOncología Médica - 23 de abril de 2024
Lectura para celebrar el Día internacional del Libro en el Hospital Quirónsalud Marbella
El objetivo de esta iniciativa es atenuar el estrés de los pacientes y fomentar el hábito de la lectura.Hospital Quirónsalud Marbella - 24 de abril de 2024
El Hospital Universitari General de Catalunya celebra el Sant Jordi con sus pacientes
El 23 de abril, el día de la rosa y el libro, también se ha celebrado en el Hospital Universitari General de Catalunya. Los pacientes ingresados han recibido una rosa junto ...Hospital Universitari General de Catalunya