The association of type 2 diabetes with overweight and obesity is so consistent that it has led to define the concept of Diabesity.
When obesity causes resistance to the action of insulin and diabetes 2 appears, we can direct the surgical technique towards the treatment of this comorbidity, in addition to achieving some weight reduction. It's what we call metabolic surgery. It is also effective in cases of hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperucemia, etc.
Diabetes causes elevation of blood sugar levels, which attacks organs such as the retina of the eye (causes blindness), the nervous system (diabetic neuropathy, impotence), the kidney (kidney failure and dialysis), blood vessels ( ulcers on the feet and amputations, heart attacks), etc.
Currently, we know that some surgical techniques are able to get Type 2 Diabetes referred, recovering health and avoiding, in most cases, taking medication or pricking insulin.
The metabolic effect of these techniques on diabetes is based on the alteration of intestinal hormones - Incretins (GLP-1, CCK, Peptide Y, ...), facilitating the action of pancreatic insulin, and correcting type 2 diabetes. they reduce certain hormones that cause the sensation of hunger (Ghrelin). The combination of these effects conditions the remission of diabetes, which is immediate after surgery.
Patients are discharged from the hospital without taking any medication in most cases, and never with insulin.
This surgery is especially indicated in patients with overweight / obesity (BMI> 30) and type 2 diabetes (resistance to the action of insulin). The best results are obtained in patients with less than 10 years of evolution of diabetes, with good pancreatic reserve (Peptide C), and who still do not need insulin, although insulin-dependent diabetics also respond well and stop taking insulin.
In Type 1 Diabetics, of autoimmune origin in which the pancreas is destroyed, this surgery can help improve glycemic control (blood sugar) and reduce insulin needs, although it is not the treatment of choice.
Metabolic surgery is effective against type 2 diabetes, improves the quality of life and is estimated to increase the life expectancy of these patients in 10 years.
Techniques
LAPAROSCOPIC VERTICAL GASTRECTOMY OR GASTRIC TUBE
What does it consist of?
Through 5 holes of less than 1 cm in the abdomen, we introduce the tweezers, the camera, and the endostaplers to be able to perform the intervention without having to open the belly, without visible scars. It consists of reducing the size of the stomach by converting it into a kind of tube, which reduces the volume of the intake. The remaining gastric remnant is extracted through the navel. It does not condition important nutritional deficits in the long term if the quality of the food is adequate.
Who is it for?
It is indicated in patients with a BMI between 35 and 45, with mild comorbidities, and with ease for dietary completion.
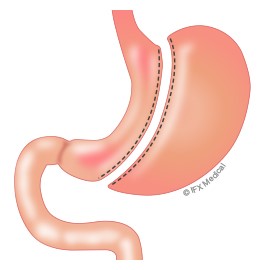
It can also be used as a first time in patients with high surgical risk or with a great excess of weight (BMI> 55) in the near future, after reducing this risk and after a great weight loss, to associate another malabsorptive procedure. Numerous times patients improve so much that they no longer need this second procedure.
When do you start to see the effect?
It conditions a loss of weight especially during the first 6 months of the postoperative period and of more than 50% of the excess in the long term.
Do you need follow-up?
He needs a later dietary control to teach the patient to eat a healthy, balanced and sufficient diet.
LAPAROSCOPIC GASTRIC BYPASS
What does it consist of?
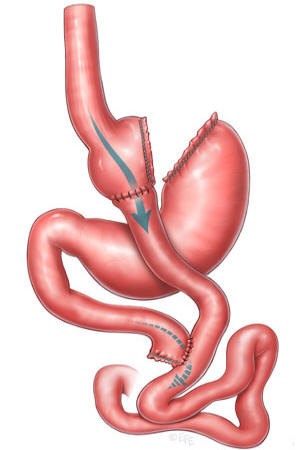
Through 5 holes of less than 1 cm in the abdomen, we introduce the tweezers, the camera, and the endostaplers to be able to perform the intervention without having to open the belly, without visible scars. It consists of the reduction of the size of the stomach (much smaller than the gastric tube) and the creation of a short circuit in the digestion. This causes the digestive juices to join with food at a later point in the digestion, which means that part of them are not absorbed, especially fats.
Who is it for?
In general, it is indicated in patients with BMI> 40, or> 35 with comorbidities. Especially BMI between 45 and 55.
When do you start to see the effect?
The most important weight loss occurs during the first 6 months, but it lasts until the year or year and a half of the intervention, at which time the weight stabilizes.
Do you need follow-up?
He needs a long-term nutritional and dietary follow-up. Otherwise, anemia (lack of iron), vitamin B12 deficiency and folic acid, lack of calcium or zinc, which may require treatment occasionally, may occur.
Monitoring is as important as intervention to achieve the greatest and most sustained loss.
The intense attention of Dr. Sala and his team in the postoperative period make the complications somewhat unusual.
The use of state-of-the-art surgical equipment, both in the operating room with the use of specific self-suturing staplers and during the postoperative period with the use of antithrombotic pneumatic stockings, makes the procedure more comfortable and reduces the risks even more.
The patient enters on the same day of the intervention, with antibiotic and thromboembolic prophylaxis. The intervention and the postoperative period proceed normally, and the patient is discharged 48 hours postoperatively with good oral tolerance and dietary information for home care until subsequent revisions.
With few exceptions, patients recover well from anesthesia and go to their room, without needing an ICU.
Do you want to know more about metabolic surgery? Look at this video
Hospital Quirónsalud Valencia
Avda. Blasco Ibáñez, 14
46010 Valencia Valencia
© 2024 Quirónsalud - All rights reserved