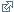
Paediatric surgery
We tell you everything you need to know about paediatric surgery: what it is, what diseases it treats and their main symptoms, the most used techniques and the operations most commonly performed. Book your consultation at one of our hospitals.

What is paediatric surgery?
Paediatric surgery focuses on the study, diagnosis and treatment of pathologies or malformations in children, from newborns to adolescents, which require a surgical approach to cure them.
This speciality provides comprehensive care for children and covers their special needs, from the information process to the actual surgical procedure.
What does paediatric surgery study?
Paediatric surgery requires a high level of specialisation, as children present very specific characteristics that require a high level of knowledge. They are not simply ‘miniature adults’. Therefore, in addition to focusing on the physiology or malformations and pathologies of children, paediatric surgeons at Quirónsalud are trained in specific areas such as:
- General paediatric surgery: deals with the most common paediatric surgical pathologies such as appendicitis, phimosis, abdominal wall hernias (umbilical or inguinal), hydrocele, thyroglossal cyst, sinus or pilonidal cyst, etc.
- Paediatric urology: addresses a wide range of conditions, including congenital malformations of the urinary tract, developmental problems of organs such as kidneys and bladder, and acquired urogenital disorders. Most notably, undescended testicle, hypospadias, obstructive hydronephrosis and so on.
- Paediatric thoracic surgery: mainly deals with the study and treatment of congenital airway and pulmonary malformations, diaphragmatic pathology, as well as congenital chest wall malformations (including pectus excavatum, pectus carinatum, etc.).
- Paediatric digestive and colorectal surgery: specialises in the surgical correction of gastrointestinal and colorectal disorders in children. This field addresses issues such as inflammatory bowel diseases, anorectal malformations and other pathologies of the entire gastrointestinal tract.
- Paediatric oncology surgery: dedicated to the diagnosis and surgical treatment of tumours and cancers in children. A multimodal approach to treatment is instrumental in childhood cancer, with paediatric oncologists and other healthcare professionals working closely together to provide comprehensive, personalised care for paediatric cancer patients.
- Plastic surgery: corrects congenital malformations, cosmetic defects, burns and other injuries in children. Examples: cleft lips, congenital ptosis, facial malformations and skin deformities.
- Maxillofacial surgery: focused on the diagnosis and surgical treatment of malformations, injuries and disorders of the facial and cranial area in children. This area addresses conditions such as cleft lip, cleft palate, mandibular deformities, and other congenital or acquired facial anomalies.
Which patients is it for?
Paediatric surgeons can make a diagnosis even before birth, and therefore they treat the foetus, and subsequently the patients, from birth until the age of 16.
Techniques, procedures and diagnostic methods
Technical advances enable a correct diagnosis to be reached quickly and surgical treatment to be carried out accurately, minimising discomfort and recovery time, which is particularly important to ensure that children are able to be active again as soon as possible. The most common procedures in this speciality include the following:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: removal of the gallbladder using a flexible catheter with a camera on the end that is inserted through two small incisions in the abdomen.
- Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC): used in critically ill patients to deliver drug therapy through the basilic or cephalic veins.
- Splenectomy: surgery to remove the spleen when it is damaged, only in cases where it has not recovered after prolonged rest.
- Appendectomy: an operation, usually laparoscopic, performed to remove the appendix with a minimal incision.
Diseases and symptoms
Main pathologies and diseases
Some of the childhood diseases that are commonly treated with surgery include:
- Phimosis
- Umbilical hernia
- Undescended testicle
- Testicular hydrocele
- Inguinal hernia
- Umbilical hernia
- Thyroglossal cyst
- Ankyloglossia (short or restrictive lingual frenulum)
- Pilonidal sinus or Pilonidal cyst
- Vascular malformations
- Congenital chest wall malformations (pectus excavatum or sunken chest, pectus carinatum, etc.)
- Pulmonary malformations
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Ovarian tumours
- Ovarian pathology
- Renal tumours
- Abdominal tumours
- Varicocele
- Cryptorchidism
- Pyeloureteral stenosis
- Hypospadias
- Oesophageal atresia
- Digestive malformations in newborns
- Gastro-oesophageal reflux
- Appendicitis
- Cholecystectomy
Related symptoms
The main symptoms children present when they come to the surgery consultation are:
- Fever
- Blemishes on the skin
- Chest pain
- Abnormal urination
- Urinary tract infections
- Abdominal pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling
- Narrowing of the foreskin
About the paediatric surgery consultation
We solve any doubts you may have before you see the specialist
Usually patients are referred to the paediatric surgery consultation by another specialist who has detected a disease or malformation that requires surgical treatment. Therefore, the surgeon assesses the situation to determine the most suitable approach and requests the necessary tests to confirm the diagnosis and perform the preoperative procedure. In addition, follow-up consultations are carried out once the child has been discharged from hospital.
What should you keep in mind?
Whenever possible, we recommend that the child answer the surgeon’s questions. This ensures that no information is lost and the specialist can interpret what the child means whenever they express themselves. It also helps children relax and makes the examination more bearable.
During the consultation, the doctor explains the procedure to the adults and clarifies any doubts they may have. On the days prior to the surgery, you will be informed about the protocol regarding the presence of accompanying persons in the hospital and during resuscitation.
What should I take to the appointment?
We recommend that you come to the consultation with the reports and results of the tests that have already been carried out, as well as a list of the symptoms that have occurred.
You may receive a questionnaire a few days before your appointment asking about your medical history, usual medication and other specific questions that will allow us to anticipate certain aspects of your consultation, helping us to expedite and personalise your care. To do this, we recommend that you download the free Quirónsalud Patient Portal application, which will facilitate communication with your healthcare team.

If you have any further questions, please contact us through the Patient Services telephone number: 900 301 013