Medical Oncology
Find out everything you need to know about Medical Oncology: what it is, its field of study, what diseases it treats and what the main treatments are. We tell you what a consultation with an oncologist involves, what to expect and what to prepare before you go. Book your appointment at one of our hospitals.
What is Medical Oncology?
Medical Oncology takes a comprehensive approach to the treatment of cancer patients in order to offer them a personalised therapy that takes into account both the clinical characteristics of the disease and other important areas of patient management, such as psychological and emotional aspects.
Oncology is a speciality that is constantly evolving and incorporating the latest scientific and technological advances to help us make the correct diagnosis and provide a specific and personalised plan of action for the patient. Treatments are increasingly more specific, more complex, and require the participation of a wide range of professionals in order to properly manage the disease in a comprehensive manner.
What does Medical Oncology study?
Medical Oncology studies the characteristics of different tumours. Cancer is a very heterogeneous group of diseases, and each disease has different biological characteristics, requiring very precise diagnostic techniques and, most importantly, cutting-edge clinical research for the development of specific drugs for the treatment of each patient. To improve diagnosis and provide the most suitable treatment, these doctors specialise in different areas or units:
- Paediatric Oncology Unit
- Lung Cancer Unit
- Breast Cancer Unit
- Digestive Tumours Unit
- Gynaecological Tumours Unit
- Genitourinary Tract Tumours Unit
- Head and neck Tumours Unit
- Sarcoma Unit
- Skin Tumours and Melanoma Unit
- Neuro-oncology Unit
- Genetic Counselling Unit
Which patients is it for?
Medical Oncology is the speciality that deals with cancer patients. Although patients are usually diagnosed by other specialists, oncologists complete the diagnosis and treat the patient with different therapies depending on tumour biology and the stage of the disease. The oncologist organises the patient’s treatment as a whole. They are the "conductor" of the orchestra, defining, at each moment, (based on a multidisciplinary approach with other specialists) the best treatment for each stage, whether it is surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy, or even referral to a clinical trial.
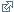
Techniques, and diagnostic methods.
The diagnostic techniques for cancer patients are many and varied. In general, radiology techniques are always required to localise the disease, such as a CAT or MRI scan, and invariably certain invasive techniques are necessary to obtain a sample of tumour tissue to make the diagnosis. This can be a CAT- or ultrasound-guided biopsy, or sometimes surgery is required to obtain the sample. Once the tissue has been extracted, the Anatomical Pathology specialists give the tumour its "full name" so that the oncologists can plan the treatment.
Diseases and symptoms
Main pathologies and diseases
The cancers most commonly treated in the Medical Oncology speciality include:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Liver cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Melanoma or skin cancer
- Thyroid cancer
- Sarcomas
- Brain tumours
- Neuroendocrine tumours
Most commonly used treatments in Oncology
Although oncology treatments are becoming increasingly sophisticated and precise, basic, major treatments are still being used to manage the disease. Broadly speaking, these are the following:
- Chemotherapy: drugs with the ability to destroy rapidly dividing cells. Tumour cells possess this characteristic, by definition. Given that chemotherapy cannot discriminate whether a cell is malignant or benign, they can also damage or destroy rapidly dividing cells in the body, such as blood, hair or nail cells.
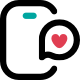
- Radiotherapy: a technique that uses ionising radiation to kill tumour cells.
- Immunotherapy: a more recently developed therapy that allows the patient’s immune system to attack tumour cells by inhibiting the "brake" that the immune system is naturally subjected to.
- Hormone therapy: very specific therapies for hormone blocking in certain tumours such as breast or prostate cancer. These are highly effective, simple treatments, but very active and essential in Oncology.
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplant: generally used in haematological tumours. This is a highly sophisticated procedure in which high-dose chemotherapy is administered to eliminate all tumour cells from a patient’s body, which requires the replacement of bone marrow cells through a transplant of stem cells from the patient’s own body or from a donor.
About the medical oncology consultation
We solve any doubts you may have before you see the specialist
Patients often come to the oncologist with referrals from other specialists and previous reports. It is important to bring all available documentation, clinical reports and radiology tests to get a full picture of the disease. During this first visit, the doctor will take a complete medical history and perform a physical examination to assess the patient, and request any additional tests that may be required. It is important to provide all the information to the oncologist, and to not be afraid to ask questions or share concerns about the diagnosis or the tests to be performed in the following days. Sometimes a treatment plan is already established in this first appointment, and the patient is informed in detail, with the pros and cons being discussed and any doubts or concerns clarified.
We advise you to come to this first appointment in the company of a family member or loved one who can offer support, help understand all the information provided, and participate in the decision-making process.
You may receive a questionnaire a few days before your visit asking about your medical history, usual medication and other specific questions that will allow us to anticipate certain aspects of your consultation, which will help us expedite and personalise your care. To do this, we recommend that you download the free Quirónsalud Patient Portal application, which will facilitate communication with your healthcare team.

If you have any further questions, please contact us through the Patient Services telephone number: 900 301 013