Microbiology and parasitology
We tell you everything you need to know about microbiology and parasitology: what it studies, what it treats and its use in medicine. Find out about its different areas of work and the main techniques it uses.
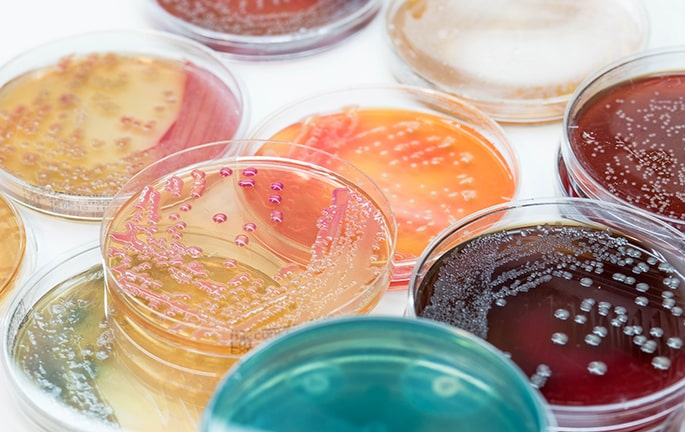
What is microbiology and parasitology?
Microbiology and parasitology handle the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases and the pathogens that cause them. The latest advances in this speciality arise from the need to respond to new situations. For example, increasing antimicrobial resistance, infections diagnosed in patients undergoing immunosuppression or the identification of new infectious agents.
Microbiologists work alongside other specialists in educating about the proper use of antibiotics, which is vital to prevent the re-emergence of diseases that were thought to have been eradicated. In addition to focusing on laboratory research, this branch of medicine also provides healthcare guidelines.
What does nuclear microbiology and parasitology study/treat?
Microbiology and parasitology help both the scientific community and the general public gain insight into the origin of diseases, which helps to prevent them and to monitor their development. Most of the efforts of these doctors focuses on early detection, as initiating treatment at an early stage of the disease is essential in most infectious diseases.
Specialists subspecialise in different branches to further their research. Most notably:
- Mycology: focused on the study of fungi, moulds and yeasts, and their detrimental effects on human health, as when these organisms take up residence in a cell, they degrade it and transform it into a substrate. This is how infections known as mycosis occur, which can be divided into superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous or systemic, affecting internal organs.
- Virology: focused on the study of viruses, acellular organisms that need to lodge in other cells in order to reproduce, and the pathologies arising from their presence in the organism. One of the most important tasks of this branch is the development of specific treatments and vaccines against viruses.
- Bacteriology: research into bacteria, prokaryotic cells, and their effects on the human body. This type of infection evolves very quickly because bacteria reproduce at high speed. However, they respond easily to antibiotic treatment.
- Parasitology. Focuses on the study of worms and protozoa that may be responsible for mild or sometimes very serious infections, such as malaria, or when they affect immunocompromised patients.
Techniques, procedures and diagnostic methods
Microbiology and parasitology procedures have advanced greatly in recent years thanks to the advent of molecular techniques and state-of-the-art equipment. However, more traditional practices continue to be one of the pillars of this speciality:
- Microscopy: techniques used to observe micro-organisms, which are impossible for the human eye to see. To magnify samples, photons of light (light microscopy) or electrons (electron microscopy) can be used to provide images with better resolution.
- Bacterial cultures: a sample of blood, urine or tissue is placed in an environment conducive to the reproduction of micro-organisms. After a period of time, the culture is observed for the presence or absence of bacteria.
- Mycological cultures: similar to the above, this technique is used to detect infections caused by fungi.
- Seeding techniques: an infectious agent is placed in a suitable environment in order to create a culture and observe its evolution. Volumetric, mass, immersion, double-layer, surface or streak seeding can be developed.
- Molecular biology techniques: these novel procedures enable faster and more reliable detection of diseases. The most basic technique is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which allows DNA fragments to be rapidly reproduced for detailed study.
- Antimicrobial susceptibility studies. Bacteria are subjected to different concentrations of antimicrobials to determine which antimicrobial may be the most suitable for treating an infection.